XMPP
M-Link User Server
XMPP Instant Messaging and Presence Server
M-Link User Server is Isode’s core Instant Messaging and Presence server based on the XMPP (eXtensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) standard. Its feature set makes it ideal for deployments where security, reliability and special functionality are vital as well as for large public deployments.
M-Link User Server can be used to support 1:1 chat, multi-user chat (MUC), Personal Eventing (PEP) and other XMPP services. M-Link User Server is used in both specialised deployments where security, reliability and special functionality are vital and in large public deployments where responsiveness, performance and scalability are paramount.
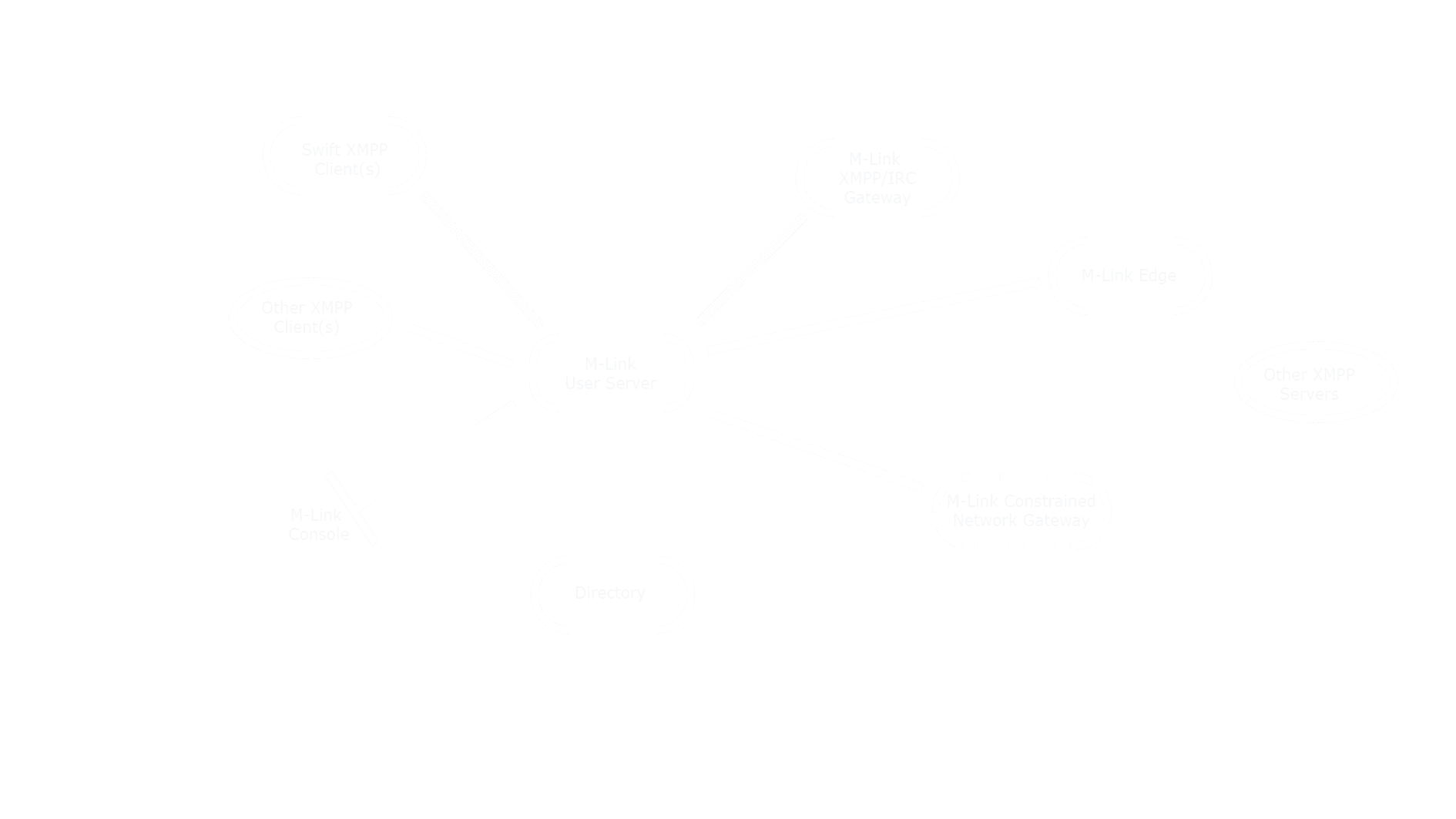
Note that the core M-Link User Server is designed for operation over internet quality links and does not support standards for operation over constrained networks, for which a separate product is available (see M-Link for Mobile Units for more information).
Key Features
Security
Security features include message security using security labels, support for data confidentiality using TLS and support for SASL authentication, Kerberos authentication and Strong Authentication (based on X.509 Public Key Infrastructure), for client/server and for server/server connections and boundary checks on message traffic using peering controls. For more information see the page on M-Link Security.
Reliability
The core XMPP model is one server per domain. A single M-Link Server can support multiple domains, with delegated administration of users within each supported domain. XMPP Clustering is a technique to enable a single domain to be supported by multiple servers. M-Link supports clustering over both Local and Wide Area Networks.
There are a number of ways in which an XMPP service can become unreliable, usually involving a failure in one or more components of the service. In a Mobile Unit deployment, where link failures can be common, Isode’s XMPP products (both the M-Link products and the Swift XMPP client) include capabilities to alert the user to and protect them from link failures. For more information see the page on M-Link Reliability.
Flexibility
Can be deployed on large public networks (jabber.org, one of the largest public XMPP installations, uses M-Link User Server), in high security environments and variations of M-Link can be used as a Boundary Guard, in Mobile Unit scenarios and as a gateway to IRC systems.
Archive and Search
M-Link has extensive archiving capabilities including search of 1:1 and multi-user chat history, export to XML archives and long-term archiving in PDF/A documents. For more information see the page on Archive and Search.
Forms Discovery and Publishing
M-Link enables flexible Forms Discovery and Publishing (FDP). FDP provides a mechanism to allow M-Link to store a list of Topics and associated form templates that can be retrieved and completed by an FDP-aware client. Once the completed form is submitted back to the Server, interested parties who have subscribed to the Topic will be immediately notified that a new instance of the form has been completed. Fore more information see the page on Forms Discovery and Publishing.
PubSub and PEP
XMPP includes a Publish/Subscribe capability to enable flexible sharing of data. Personal Eventing is a subset of this, which allows a user to publish and share data, and in particular “extended presence” information. Personal Eventing is expected to be the basis of important XMPP developments, and support is starting to appear in XMPP clients and applications. M-Link supports Publish/Subscribe and PEP is supported using Publish/Subscribe. Further information on Publish/Subscribe can be found in the whitepaper [XMPP PubSub].
BOSH
BOSH (XEP-0124: Bidirectional-streams Over Synchronous HTTP) is a mechanism to operate XMPP over HTTP. This facilitates development of Web XMPP clients running in a browser. M-Link supports BOSH in the core server.
Peering Controls
M-Link provides a number of peering controls, controlling what is sent to and received from other XMPP peer servers. Key controls are security label checks & transformations, filtering of traffic types and ‘folding’ of messages and presence data to remove selected information. Peering controls, which are available in all M-Link products, are described in more detail on the M-Link Edge product page.
Management
An M-Link Server maintains its own configuration, which a suitably privileged client can view or modify using XMPP commands. Isode provides a GUI tool, M-Link Console (MLC), which manages this configuration over XMPP, provides server control and monitoring services. User accounts are held in a Directory, with Active Directory or Isode’s M-Vault being popular choices. User accounts in the Directory can be managed externally and Isode provides administration tools for this purpose.
Monitoring of server and system performance can be done using MLC, a Web Application and by SNMP (integrating server monitoring with Enterprise monitoring of network and application components). More information can be found on the page on Configuration and Oprational Management.
Use of Directory
M-Link uses Directory to hold user authentication information. This will often be an external enterprise directory using standard schema that has already been set up. A common choice for those not using M-Vault for this purpose is Microsoft’s Active Directory. By using the directory for authentication, M-Link can share authentication credentials and authentication management with other applications that make use of the same infrastructure
XMPP users have a ‘profile’ that contains information about the user, such as the user’s name, nickname and phone number. M-Link provides capabilities to manage this information in conjunction with equivalent information held in the authentication directory.
M-Link provides support for general LDAP groups as well as for Active Directory groups configured in the authentication directory. Groups can also be configured in the configuration directory, giving the option to define a group by an LDAP search, which can allow groups to be specified without duplicating information. Groups can be used for two purposes:
- Roster Pre-Population.
- MUC (Multi-User Chat) access control.
Isode has incorporated into the M-Link User Server, M-Link Edge, M-Link IRC Gateway and Mobile Unit variations features that make them the natural choice for instant messaging and presence in military, intelligence and government deployments. These features include message security using security labels, support for data confidentiality using TLS and support for SASL authentication, Kerberos authentication and Strong Authentication (based on X.509 Public Key Infrastructure), for client/server and for server/server connections and boundary checks on message traffic using peering controls.
Security Labels
Messages can be given Security Labels. Security Labels are used to control whether an entity (such as a user or a MUC) may access a message. The entity’s Security Clearance is used to determine whether it may see a message with a given Security Label.Isode supports security labels according to XEP-0258 (Security Labels in XMPP) with support for S/MIME ESS Labels (RFC 2157 – Enhanced Security Services for S/MIME) and for Isode XML Labels. Controls are based on Security Clearance of Sender, Recipient, and peer XMPP server. Security Label based controls are also provided for Multi User Chat (MUC). In the screenshot below security labelled chat in a multi-user chat room is shown from the perspectives of two different users with differing security clearances (in this example Isode’s Swift XMPP Client is used).
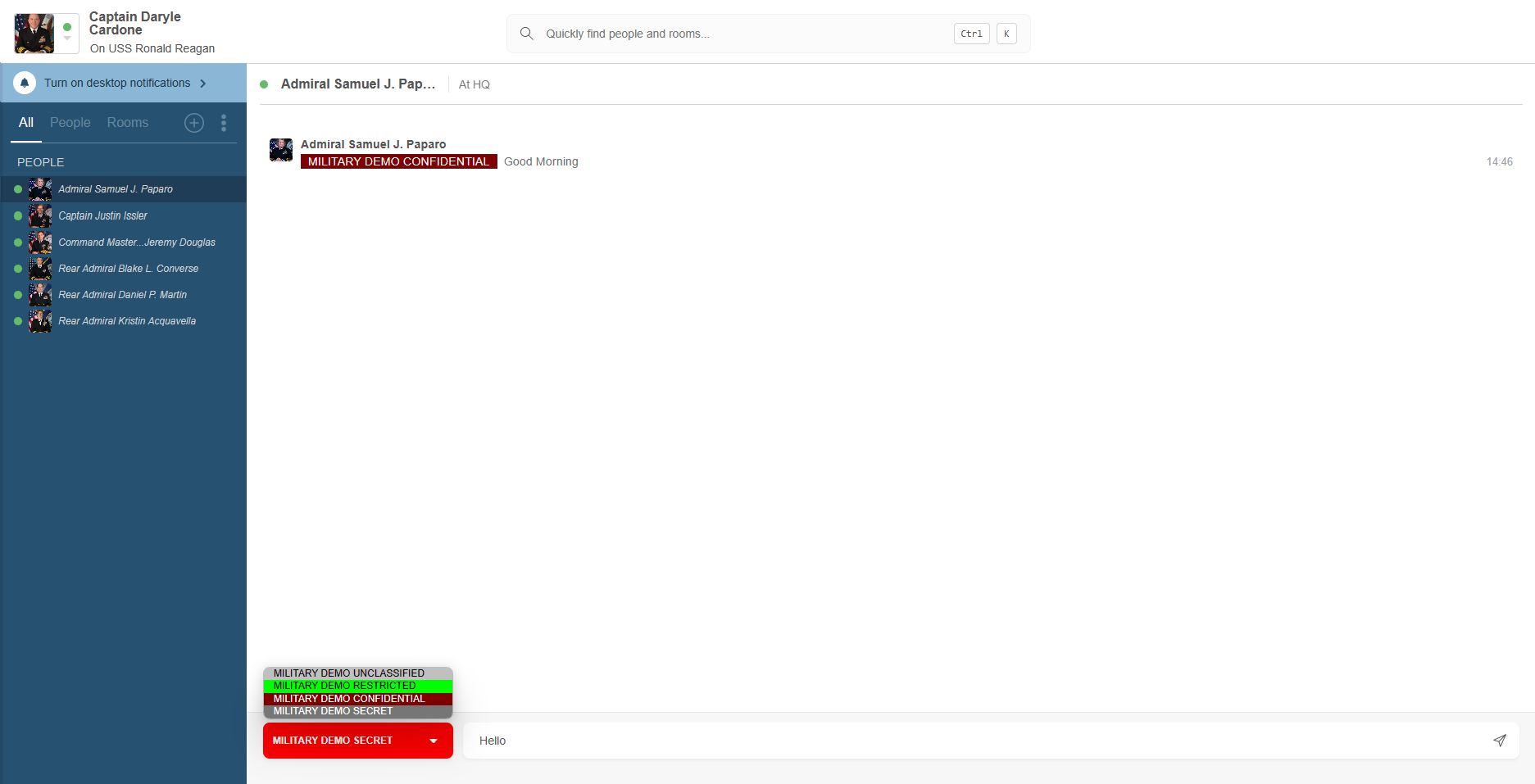
Client/Server support for XEP-0258 is provided, in particular for the discovery mechanism that enables an XMPP client to determine which Security Labels can be used for a specific destination. Default (per server or per domain) catalogs can be configured and personal catalogs, stored in the directory, are also supported so that users can customize their own set of security labels. Overall control is Security Policy based, using the mechanisms described in the product page covering Isode’s Security Policy Infrastructure.
M-Link products support a number of features designed to provide interoperability, to the extent feasible, between the XEP-0258 security label services and CDCIE Client Chat Protocol clients like TransVerse and JChat. Further information is given in the Isode whitepaper, [Using Security Labels to Control Message Flow in XMPP Services].
Working with Clients/Servers with no Security Label Support
To support deployments in mixed environments, where some servers and clients do not support security labels, M-Link products support:
- Default Labels: these can be configured for servers, peers, MUC rooms or services (i.e. applied to one domain within a single server supporting multiple IM domains).
- FLOT (First Line of Text) labels: this allows for the insertion of a label at the start of any XMPP message, using the text from the XEP-0258 display marking. This ensures that clients not capable of XEP-0258 support will see security labels.
Authentication
XMPP Client/Server authentication uses SASL, enabling a number of authentication mechanisms. Password based mechanisms, which should always be used over TLS, are PLAIN and SCRAM (Salted Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism) with SCRAM being the recommended password based mechanism. For more on SCRAM see the Isode whitepaper [SCRAM: A protocol for Password Authentication].
Kerberos authentication is supported following XEP-0233 which includes support for clustered access and multi-domain. See the Isode whitepaper [Isode Support for Kerberos, Active directory and Single Sign On] for more information.
Strong Authentication, based on X.509 Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), is supported for client/server and for server/server connections. This is preferable to the default server dialback mechanism. Strong authentication uses SASL EXTERNAL authentication which in turn uses X.509 authentication at the TLS level. Isode products, including M-Link, Swift, and Sodium CA, support XMPP-specific Subject Alternative Names as detailed in RFC 6120 as well as more commonly used Subject Alternative Names such those for DNS names and email addresses. Flexible mappings facilitate client use of smart cards. Strong Authentication includes directory based path discovery and CRL checking and is compliant to RFC 5280. Server private keys can be held securely in the M-Link server or in the Windows Certificate Store. Strong Authentication is recommended for secure deployments. Data integrity and confidentiality protection can be provided either by TLS or by SASL/Kerberos.
FIPS 140-2
FIPS 140-2 is a US Government specification relating to the use of cryptography in computer software. M-Link products provide a FIPS 140-2 compliant mode of operation which ensures that only certified implementations of approved cryptographic algorithms are used.
Peering Controls
M-Link’s peering controls allow for boundary checks on both inbound and outbound server to server XMPP traffic. These include:
- Control as to who can be peered with (either an explicit grant list, or any peer with an explicit deny list).
- Control over the level of authentication required for each peer (e.g., Strong Authentication).
- Application of access controls based on a Security Label with the message and a Security Clearance associated with the peer.
- Transformation of security labels, including FLOT label mappings.
- Presence Folding, which enables presence information to be filtered to reduce the information shared.
- Message Folding, which enables fields in XMPP messages to be filtered to reduce the information shared.
- Prevention of certain types of messages, such as MUC or Chat State Notifications.
- Constraint to MUC only or 1:1 chat only.
- Prevention of in-band file transfer and negotiation of out of band file transfer.
Use of peering controls is described in two Isode whitepapers. [XMPP Boundary and Cross Domain Protection] looks at applying boundary controls using peering and [Peering Controls in M-Link and M-Link Edge] looks at peering controls in more detail. Whilst peering controls are the simplest way to apply boundary controls, use of an XMPP Boundary Guard (such as M-Link Edge), gives a number of advantages over this approach by enabling controls to be applied and checks made separate to the XMPP server.
On this page you’ll find information on features designed to minimise the impact of Server Failures and/or Link Failures in order to provide a reliable XMPP service. M-Link offers LAN and WAN clustering to protect against potential server failures as well as reliable messaging features to address the consequences of link failure.
Server Clustering
The core XMPP model is one server per domain. A single M-Link Server can support multiple domains, with delegated administration of users within each supported domain. XMPP Clustering is a technique to enable a single domain to be supported by multiple servers. Server Clustering is a feature of the M-Link User Server product. Clustering is not supported for M-Link IRC Gateway or M-Link Edge. M-Link Edge may be deployed in an active/active configuration, which does not need clustering.
XMPP clustering needs to synchronize ‘state’ between servers to ensure that messages are routed to correct destinations and that presence information is correct. It is also important that information from various services (Presence, Multi User Chat (MUC), and Publish Subscribe (PubSub)) are set on the local server where possible. For example, where MUC subscribers are on multiple servers, participant groups should be managed locally on each server, and messages sent directly to other local users without having to go to another server first. A related characteristic is that MUC and PubSub will continue operation in the event of any cluster node failing.
Isode’s XMPP Clustering implementation is designed to work well for both LAN Clustering and Wide Area Clustering environments. While M-Link Clustering may be used with many nodes, Isode generally recommends deployment of two node clustering. It is strongly recommended to review with Isode when considering clusters of more than two nodes.
Local Area Network (LAN) Clustering
In LAN Clustering there are multiple clustered XMPP servers operating on a common fast highly reliable local network. Clustering in this environment is important for large deployments, as it enables servers to be added to support load levels greater than can be handled by a single server. This horizontal scaling is important for service providers and large enterprises. It also provides reliability, so that service can continue in the event of failure (accidental or planned) of a server.
Wide Area Network (WAN) Clustering
In Wide Area Clustering the XMPP servers are interconnected by links that may be slower and less reliable than a LAN. There are various scenarios where this is important:
- Off site operation of a server, so that service can continue in event of site failure (Disaster Recovery).
- Support of organizations with multiple sites, so that a server can be run at each site.
- Support of a distributed military deployment with, for example, one server at HQ and another in the field.
Supporting Wide Area Clustering requires protocols and algorithms that will deal with wide area network throughput/latency and periods where connectivity is lost. Servers need to be kept in sync, but operations should continue as well as possible when there are network failures.
Having a server close to a client with good connectivity will give a fast and robust client experience. It is important that local traffic is optimized, and does not switch between servers except where needed. Handling traffic locally to a server without unnecessary switching is particularly important for Wide Area Clustering.
Reliable Messaging
There are a number of ways in which an XMPP service can become unreliable, usually involving a failure in one or more components of the service. In a constrained network deployment, where link failures can be common, Isode’s XMPP products (both the M-Link server and the Swift XMPP client) include capabilities to alert the user to and protect them from link failures.
Message Acknowledgements
Users of messaging systems (email or instant messaging) operating in environments with internet quality links often make the usually justified assumption that a message has been delivered. Users in constrained networking environments, where link failures are common, cannot afford to make that assumption.
M-Link and Swift both support XEP-0198: Stream Management for message acknowledgements clearly showing the status of messages and allowing the user to decide on remedial action in the event of non-delivery.
Federated Multi-User Chat
In standard Multi-User Chat (MUC) a room is hosted on one server and participants joining the room may be local to that server or joining via another server using standard XMPP server federation. A link failure will disrupt the ability of users on a federated server to participate in the MUC.
M-Link supports XEP-0298: Federated MUC for Constrained Environments, federating the provision of MUC, just as the distribution of XMPP servers federates the provision of 1:1 chat. More information on Federated Multi-User Chat can be found in the whitepaper [Federated Multi-User Chat: Efficient and Reliable Operation over Slow and Unreliable Networks].
M-Link has extensive archiving capabilities including search of 1:1 and multi-user chat history, export to XML archives and long-term archiving in PDF/A documents. This page describes those capabilities including architecture, end-user access archives, and configuration & management.
The diagram below illustrates the M-Link Search and Archive architecture. An archive process will usually run on the same machine as the core M-Link server. In a clustered configuration, an archive process will run on each cluster node, and there is an archive clustering protocol that connects those processes, so that each holds information from each cluster node.
End user access to the cluster is provided using the protocol specified in XEP-0313: Message Archive Management (MAM) for both standard XMPP Clients and web access using XEP-0206: XMPP over BOSH. M-Link Console, the M-Link Management GUI, connects directly to an M-Link Archive process to provide operator access to the archives for other search and archive management capabilities.
Further information on search and archive architecture used by M-Link can be found in the whitepaper [M-Link Archive and Search].
End-User Access
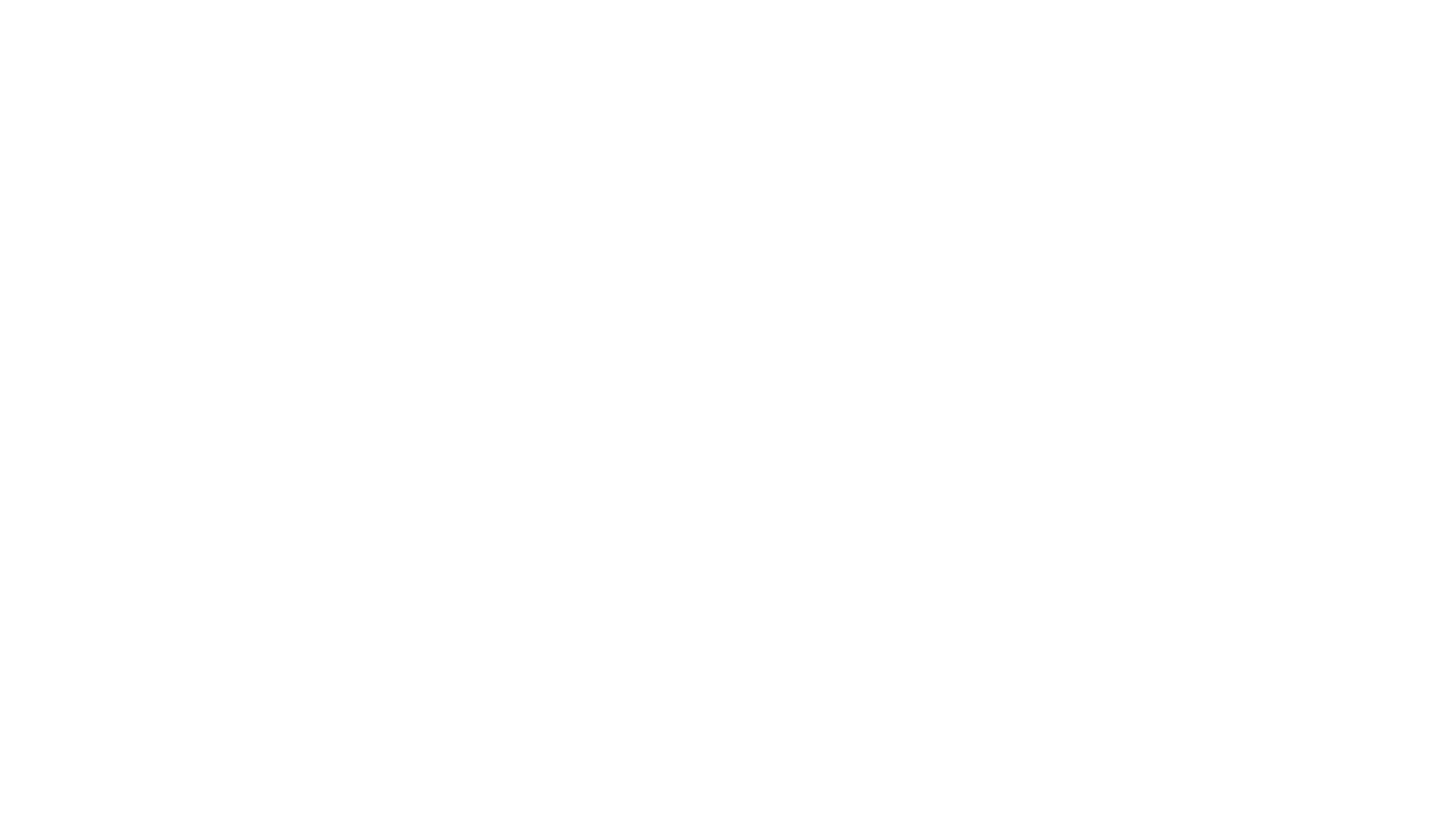
Message Archive Management (MAM) operates over the standard XMPP Client to Server protocol and XMPP Clients that implement MAM can directly access M-Link to search and access XMPP archive information. MAM provides a number of capabilities, including:
- Access to the key XMPP message types:
- 1:1 User Chat.
- MUC (Multi-User Chat).
- PubSub (Publish/Subscribe).
- Selection of messages over a date/time range.
- Filtering by user and free form text.
- Paged results to deal with large search results.
In many XMPP deployments some or all of the XMPP Clients may not yet support MAM. For those deployments (and for situations where web access to XMPP and other services is the preferred route) Isode supplies a web interface to MAM in the form of the Message Archive Browser. More information can be found in the whitepaper [XMPP Archive and Search].
The M-Link MAM web application allows the user to select MUC or 1:1 chats, and then search over a selected time range.
Configuration and Management
Configuration and management of archives is done using M-Link’s management GUI, M-Link Console (MLC). Capabilities include:
- Archive configuration and selection of data to be archived.
- Search of all archived data including:
- Search refinement
- Zoom, to see activity around a specific record
- Save search as PDF/A
- Expire data from archive older than a certain age.
- Redact data, to remove sensitive information from the archive.
Archives
M-Link Console also provides an option to archive messages into separate XML files which are organized by date, user and MUC room. These files cover activity over one day. The archive files themselves are an XML representation of the messages exchanged. These can be processed in any way desired. M-Link Console provides a GUI to browse and render archived messages in the audit files. Archiving can be configured independently for 1:1 messages and MUC messages.
Where M-Link is providing critical services for which there is a need to record activity for a long period, such records need to be stored in a format that will be usable many years in the future. To support this, MLC allows for export of archives to PDF/A documents. PDF/A is an ISO-standardized version of the Portable Document Format (PDF) specialized for the digital preservation electronic documents.
M-Link enables flexible Forms Discovery and Publishing (FDP) using protocol described in XEP-0346. FDP provides a mechanism to allow M-Link to store a list of Topics and associated form templates that can be retrieved and completed by an FDP-aware client. Once the completed form is submitted back to the Server, interested parties who have subscribed to the Topic will be immediately notified that a new instance of the form has been completed.
Forms are widely used in military operations, where there is a need to handle forms (such as Medical Evacuation or “MEDEVAC” forms) quickly and share completed forms with a large number of parties who may need to take action, such as helicopter services, emergency vehicles and medical facilities. The FDP capability is shipped as part of the M-Link User Server and the M-Link Mobile Unit Server.
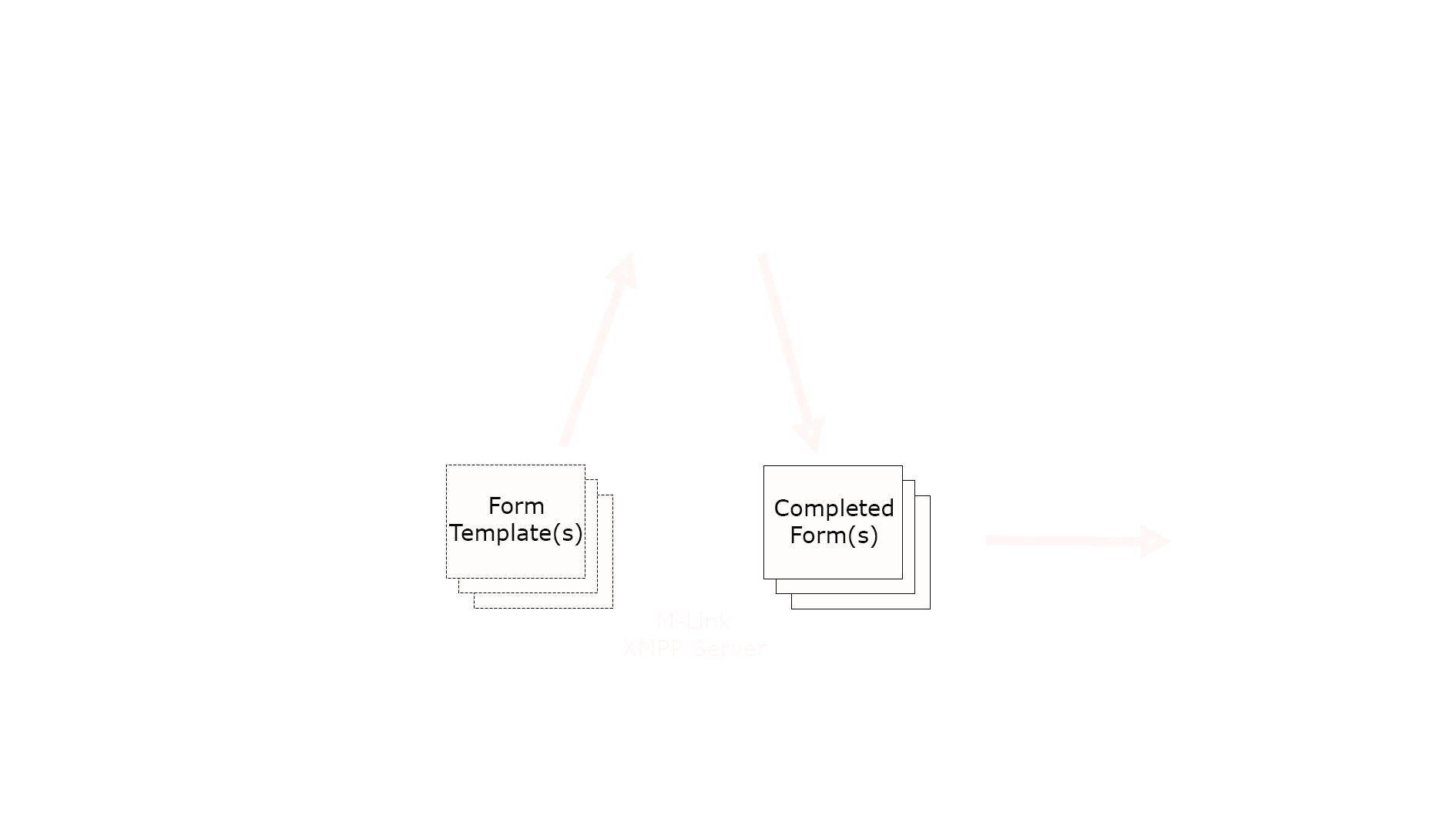
As illustrated in the diagram above, the FDP process is:
- A Topic (such as MEDEVAC) and associated form template is created using M-Link Console.
- A FDP Client discovers the Topic and, using the provided form template, submits a completed form back to the Server.
- The Server notifies any interested parties (Subscribers to the Topic) that a new completed form has been submitted, allowing them to request a copy of the completed form. Subscriptions to Topics and publishing of completed forms is achieved using XMPP PubSub.
Topic/Forms Creation & Management
The FDP service as well as the FDP Topics and form templates can be configured using the M-Link Console management GUI.
- Create an FDP Domain to hold one or more Topics
- Add, edit and remove FDP Topics and associated form templates
- Setting stylesheets for Topics, which may be used by some FDP Clients to transform submitted forms into another format
- Define who is allowed to complete and publish forms (such as users defined by their JID and/or all users at specified domains)
- View and test form templates
- View published forms
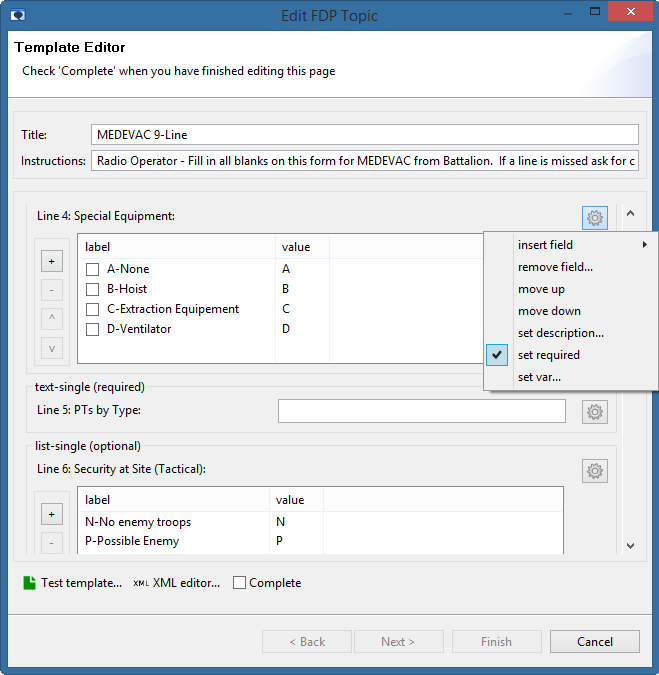
Forms Publishing & display (FDP client)
Isode provides an FDP client as a Web Application to discover and publish forms. This web application, which is shipped with all M-Link variations that include the FDP capbility,allows a user to:
- Obtain a list of available Topics (and associated form templates).
- Select a Topic, fill in the form and publish it.
- Subscribe to one or more topics, review published forms and be alerted to new forms.
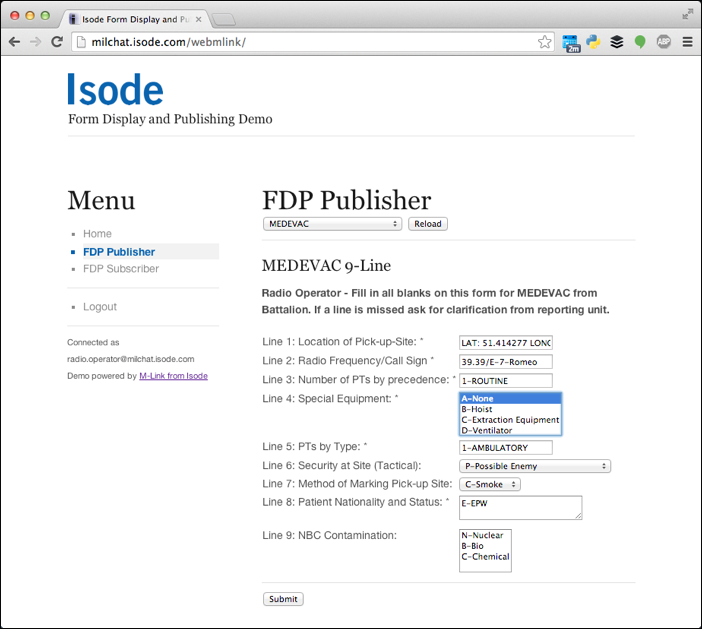
Other FDP capable clients, such a NATO’s JChat client, may also be used for both publish and subscribe purposes. Background to this requirement and a more detailed description of the M-Link FDP support are provided in the whitepaper [Military Forms using XMPP].
An M-Link Server maintains its own configuration, which a suitably privileged client can view or modify using XMPP commands. Isode provides a GUI tool, M-Link Console (MLC), which manages this configuration over XMPP, provides server control and monitoring services. User accounts are held in a Directory, with Active Directory or Isode’s M-Vault being popular choices. User accounts in the Directory can be managed externally and Isode provides administration tools for this purpose.
Monitoring of server and system performance can be done using M-Link Console, or a custom Web Application.
M-Link Console
MLC’s setup wizard allows administrators to quickly setup a single or multi-node (clustered) XMPP service. M-Link requires a Directory to hold user and group information. MLC enables the setup of an M-Vault Directory to be used in conjunction with M-Link for this purpose and also allows for the utilisation of an existing LDAP Directory, including Microsoft Active Directory.
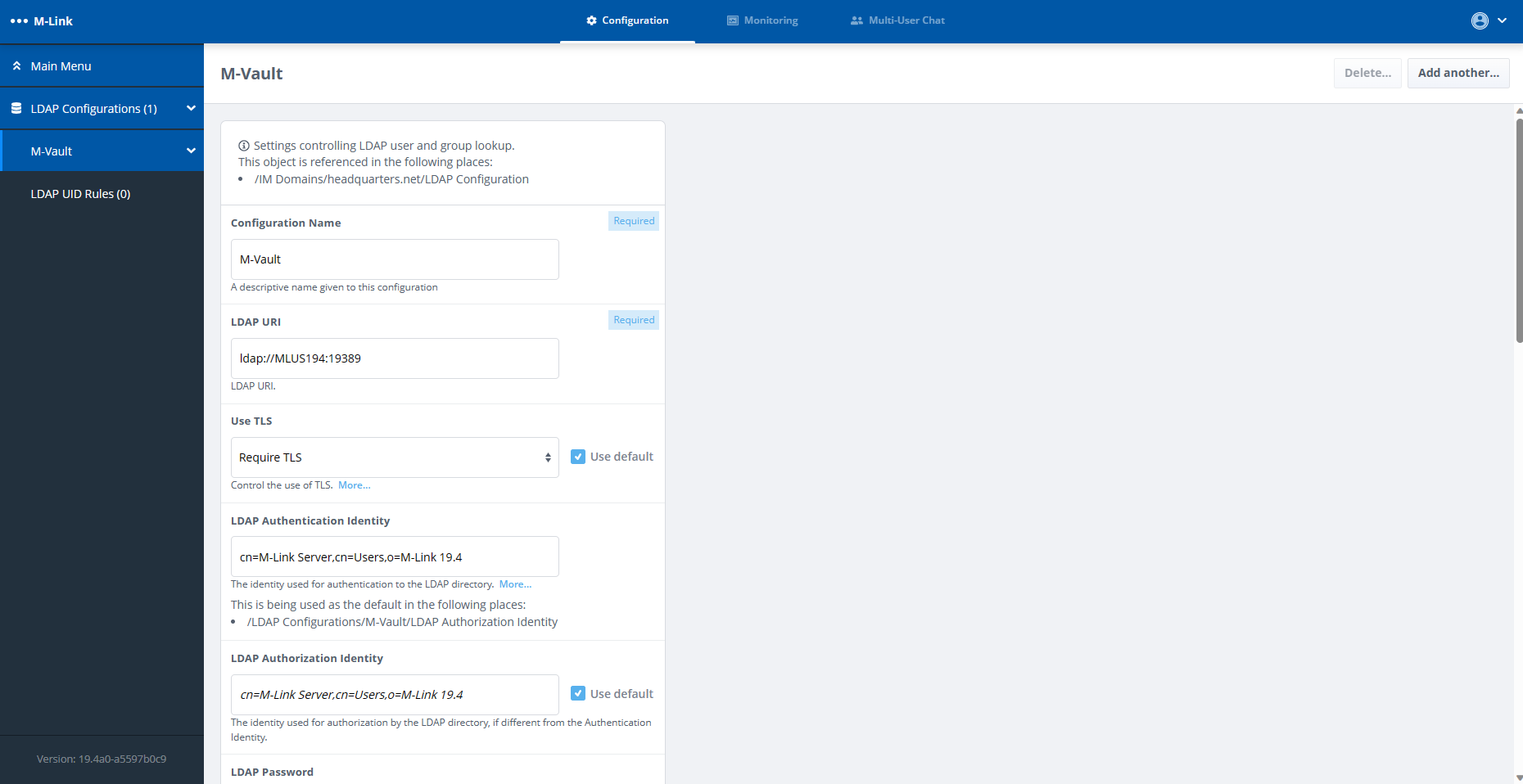
MLC provides a “System Diagnostics” view, to make checks on the local machine & validate configuration and can can start and stop M-Link servers on Windows, Solaris and Linux. A Security Check List , for both node and service, warns the operator of any settings which may suggest security risks.
Clustering
A typical M-Link deployment will be provided by multiple servers operating in a clustered configuration to provide reliability. M-Link Console provides management at both service and cluster node level. Most management is done at the service level, with configuration changes automatically affecting all nodes. Some functionality is available the node level, including:
- Statistics information on the performance of each node.
- Option to perform node-specific configuration, which may be useful for advanced deployments. When this is done, the UI shows clearly where node options are set differently to the service wide default.
- Configuration changes that need to adjust node-specific files (e.g., setup of private keys for TLS)
MLC validates that the nodes in a cluster have consistent configuration and status. More information on clustering can be found on the M-Link: Clustering & Reliability page.
Security Labels
MLC enables configuration of M-Link Security Label capabilities, including setting up Security Label Catalogs, and configuring Security Labels associated with MUC Rooms and Domains. See the M-Link: Security page for more information.
TLS & X.509 PKI
MLC enables setup and configuration of Strong Authentication for TLS and for peer authentication, by configuring an X.509 identity and associated PKI and TLS parameters for each server. Identity setup makes use of CSRs (Certificate Signing Requests) to interact with a Certification Authority. Trust anchors can be configured manually, or make use of the Windows Certificate Store defaults. MLC can use strong authentication to connect to M-Link, including use of Smart Cards.
Components, IM, MUC and PubSub domains
M-Link can support multiple domains, which can be used for multiple purposes (IM, MUC, or PubSub). MLC enables setup and management of these domains. Domain management can also be used to configure XEP-0114 components to integrate third party services. For MUC domains, MLC provides detailed MUC administration view, so that MUC rooms can be created and managed from MLC as part of an M-Link service.
Groups
MLC provides a tab for managing groups, which are important in most XMPP services. There is a special operator group (for users that can manage the M-Link service) and a range of custom groups. Groups can be defined as an explicit list, as an LDAP search, or reference a Directory group (AD Group or LDAP Group). Groups can be referenced for MUC access control, and can be used to provide roster pre-population, or to enable administration configuration of user rosters.
Peering Controls
M-Link Edge makes use of peering controls to control how messages are routed and to control message flow. The Peering Configuration tab enables setup of routing configuration, filtering and controls associated with the peer. Link control enables use of special protocols between a pair of M-Link servers, in particular:
- XEP-0361, to reduce handshaking on slow links.
- STANAG 5066 for use over HF Radio.
- Custom integration for use with High Assurance Guards.
User Account Management
Users of an M-Link server or service will be configured in a Directory. User provisioning may be handled independently of M-Link, for example when using a third party directory such as Microsoft Active Directory. Isode provides an integrated approach from M-Link Console to support user provisioning, which uses direct access to M-Vault over LDAP. This enables:
- Adding/Disabling Accounts.
- Deletion of Accounts, either permanently or by “tomb stoning” and use of “tomb stones” to warn operator about creating accounts with a name that has been previously used.
- Display account “last use” time and auto-disable accounts after configurable period
- Removal of M-Link rosters from deleted and/or “tomb stoned” accounts.
Monitoring
MLC connects to an XMPP service, and can provide a range of monitoring information including general service status & uptime, information on connected users & peers, general server statistics and detailed performance information. Multiple XMPP services can be monitored, including limited monitoring of XMPP servers other than M-Link.
Web Application
An M-Link Web Application is available which provides an overview of some key statistics for the M-Link Server, displaying a graph for each statistic and a summary of the current values in a table.
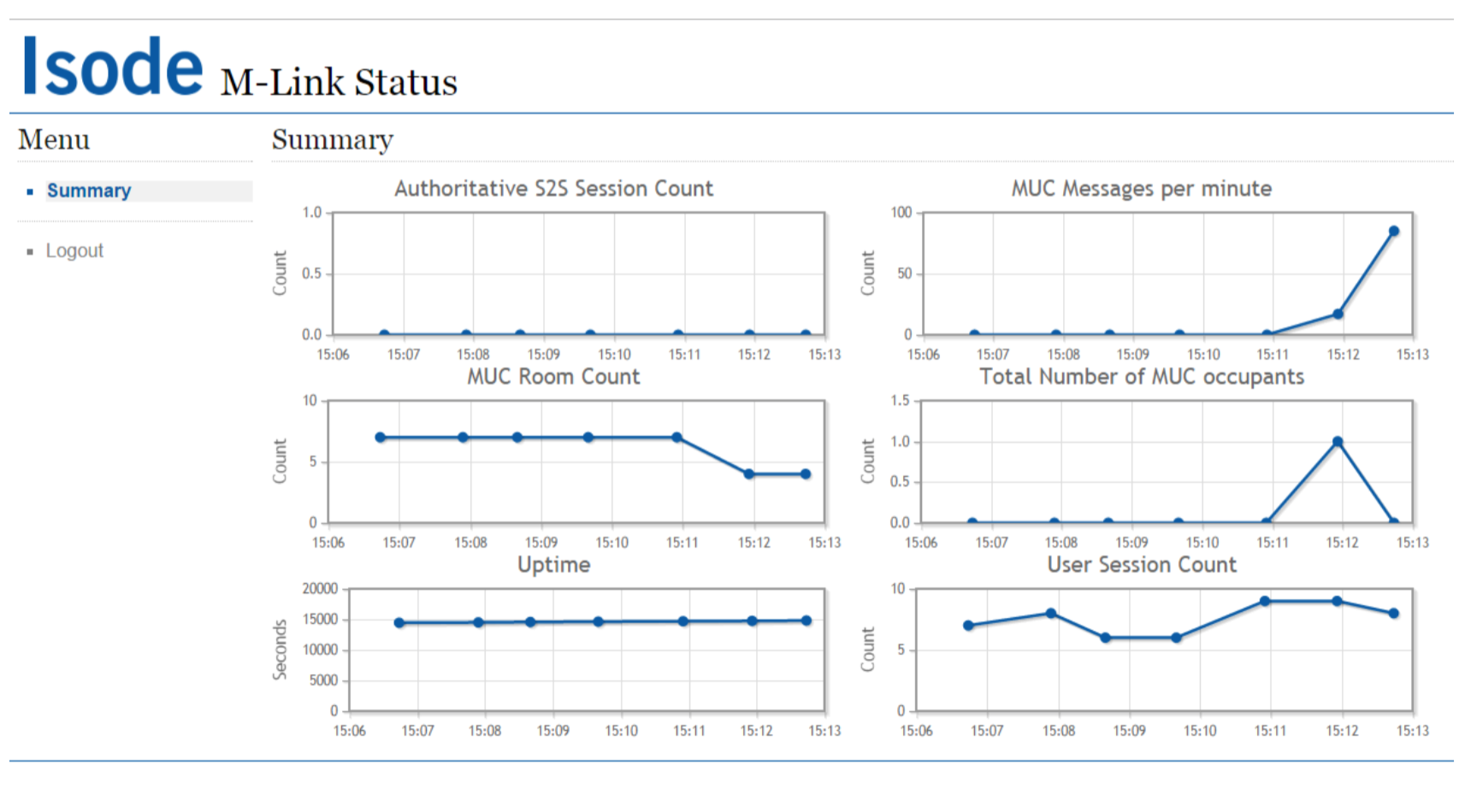
These include the authoritative server-to-server (S2S) session count, MUC messages per hour, MUC room count, total number of MUC occupants, server uptime and user session count. The charts are updated automatically, at a regular time interval determined by the M-Link Server.
The involvement of Isode and Isode staff members in Standards settings bodies such as the IETF and the XMPP Standards Foundation (XSF) has resulted in a long list of RFCs, XEPs and Internet Drafts authored or edited by Isode staff members. M-Link Open Standards conformance is listed below.
| RFC 2634 | Enhanced Security Services for S/MIME. P. Hoffman, June 1999 |
| RFC 2788 | Network Services Monitoring MIB. S. Kille, N. Freed, March 2000 |
| RFC 6120 | Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP): Core. P. Saint-Andre, March 2011 |
| RFC 6121 | Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP): Instant Messaging and Presence. P. Saint-Andre, March 2011 |
| RFC 6122 | Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP): Address Format. P. Saint-Andre, March 2011 |
| RFC 6125 | Representation and Verification of Domain-Based Application Service Identity within Internet Public Key Infrastructure Using X.509 (PKIX) Certificates in the Context of Transport Layer Security (TLS). P. Saint-Andre, J. Hodges, March 2011 |
| XEP 0004 | Data Forms. J. Hildebrand, J. Miller, R. Eatmon, T. Muldowney, P. Saint-Andre, August 2007 |
| XEP 0012 | Last Activity. J. Miller, T. Muldowney, P. Saint-Andre, November 2008 |
| XEP 0030 | Service Discovery. J. Hildebrand, P. Millard, R. Eatmon, P. Saint-Andre, February 2007 |
| XEP 0045 | Multi-User Chat. P. Saint-Andre, July 2008 |
| XEP 0049 | Private XML Storage. P. Saint-Andre, R. Davies March 2004 |
| XEP 0050 | Ad Hoc Commands. M. Miller, June 2005 |
| XEP 0054 | vCard Profiles. P. Saint-Andre, March 2003 |
| XEP 0060 | Publish-Subscribe. P. Millard, P. Saint-Andre, R. Meijer, July 2010 |
| XEP 0068 | Field Standardization for Data Forms. P. Saint-Andre, Joe Hildebrand, July 2004 |
| XEP 0077 | In-Band Registration. P. Saint-Andre, January 2006 |
| XEP 0078 | Non-SASL Authentication (for support of older clients). P. Saint-Andre |
| XEP 0082 | XMPP Date and Time Profiles. P. Saint-Andre, May 2003 |
| XEP 0091 | Legacy Delayed Delivery. P. Saint-Andre, May 2009 |
| XEP 0092 | Software Version. P. Saint-Andre February 2007 |
| XEP 0114 | Jabber Component Protocol. P. Saint-Andre, March 2005 |
| XEP 0124 | Bidirectional-streams Over Synchronous HTTP (BOSH). Ian Paterson, Dave Smith, Peter Saint-Andre, Jack Moffitt, Lance Stout, Winfried Tilanus, November 2016 |
| XEP 0128 | Service Discovery Extensions. P. Saint-Andre, October 2004 |
| XEP 0131 | Stanza Headers and Internet Metadata. P. Saint-Andre J.Hildebrand, July 2006 |
| XEP 0133 | Service Administration. P. Saint-Andre, August 2005 |
| XEP 0138 | Stream Compression. J. Hildebrand, P. Saint-Andre September 2007 |
| XEP 0163 | XPersonal Eventing via Pubsub. P. Saint-Andre, K. Smith September 2007 |
| XEP 0198 | Stream Managament. J. Karneges, June 2011 |
| XEP 0199 | XMPP Ping. P. Saint-Andre, June 2009 |
| XEP 0203 | Delayed Delivery. P. Saint-Andre, September 2009 |
| XEP 0212 | XMPP Basic Server 2008. P. Saint-Andre, July 2007 |
| XEP 0220 | Server Dialback. P. Saint-Andre, J. Miller, December 2007 |
| XEP 0227 | Portable Import/Export Format for XMPP-IM Servers. M. Henoch, W. Hussain, March 2010 |
| XEP 0233 | XMPP Server Registration for use with Kerberos V5. M. Miller, P. Saint-Andre, J. Hildebrand, M. Verma, March 2017 |
| XEP 0237 | Roster Versioning. Peter Saint-Andre, D. Cridland, March 2010 |
| XEP 0243 | XMPP Server Compliance. P. Saint-Andre, September 2008 |
| XEP 0258 | Security Labels in XMPP. K. Zeilenga, March 2009 |
| XEP 0270 | XMPP Compliance Suites. P. Saint-Andre, September 2009 |
| XEP 0289 | Federated MUC for Constrained Environments. K. Smith, May 2012 |
| XEP 0313 | Message Archive Management. K. Smith, M. Wild, July 2018 |
| XEP 0352 | Client State Indication. M. Wild, November 2018 |
| XEP 0361 | Zero Handshake Server to Server Protocol. S. Kille, July 2015 XEP-0361 is only used by M-Link Edge (for some integrations with High Assurance Guards), M-Link Mobile Unit Server and M-Link Mobile Unit Gateway. |
| XEP 0363 | HTTP File Upload. Daniel Glutsch, January 2022 |
| XEP 0365 | Server to Server communication over STANAG 5066 ARQ. S. Kille, September 2015 XEP-0365 is only used by the M-Link Mobile Unit Server and the M-Link Mobile Unit Gateway. |
Ready to request an Evaluation?
Thankyou for considering Isode’s software products. To request an evaluation, please select the product(s) you are interested in, then fill out the enquiry form.
Select your Evaluation products:
Customer Portal
For access to our customer portal please login below.
If you are having trouble accessing the portal, please contact our support team who will be happy to help.
Need help with your account? Contact us
