Products
Cross Domain Guards
Cross Domain Guards that provide an extra layer of security into your networks.
Security Conscious Cross Domain
Keep your network boundaries locked down and your teams communications secure with purpose made boundary guards.
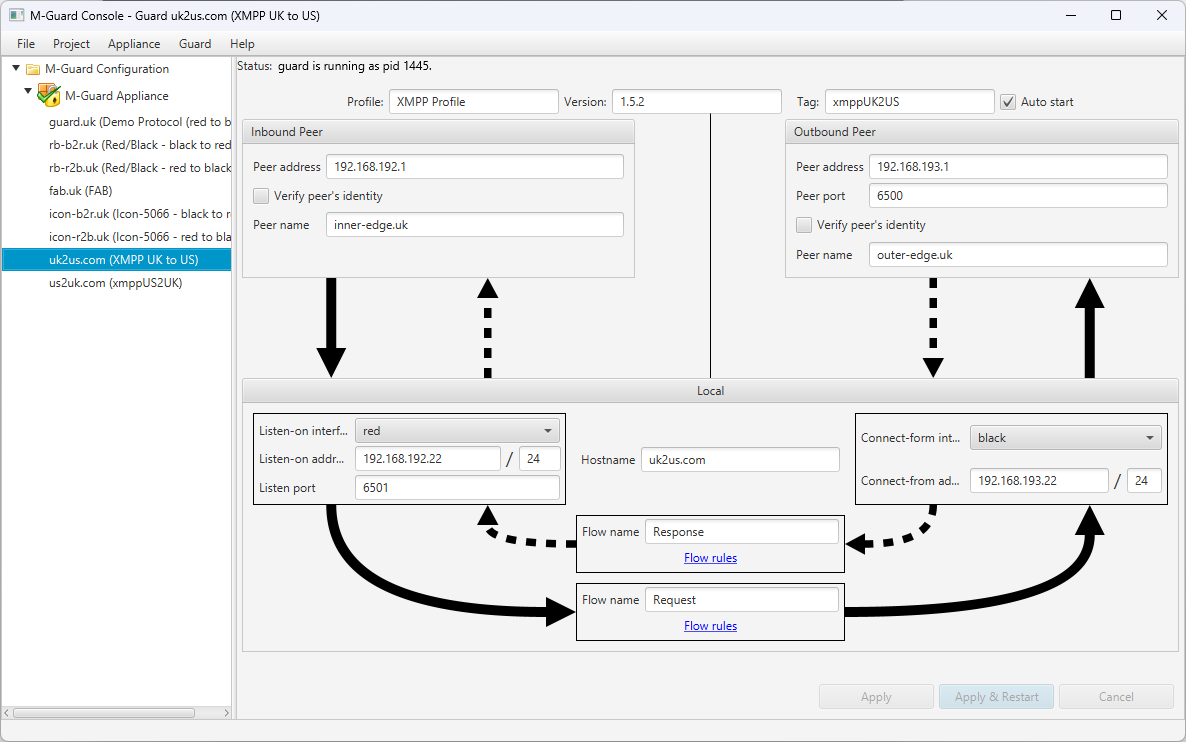
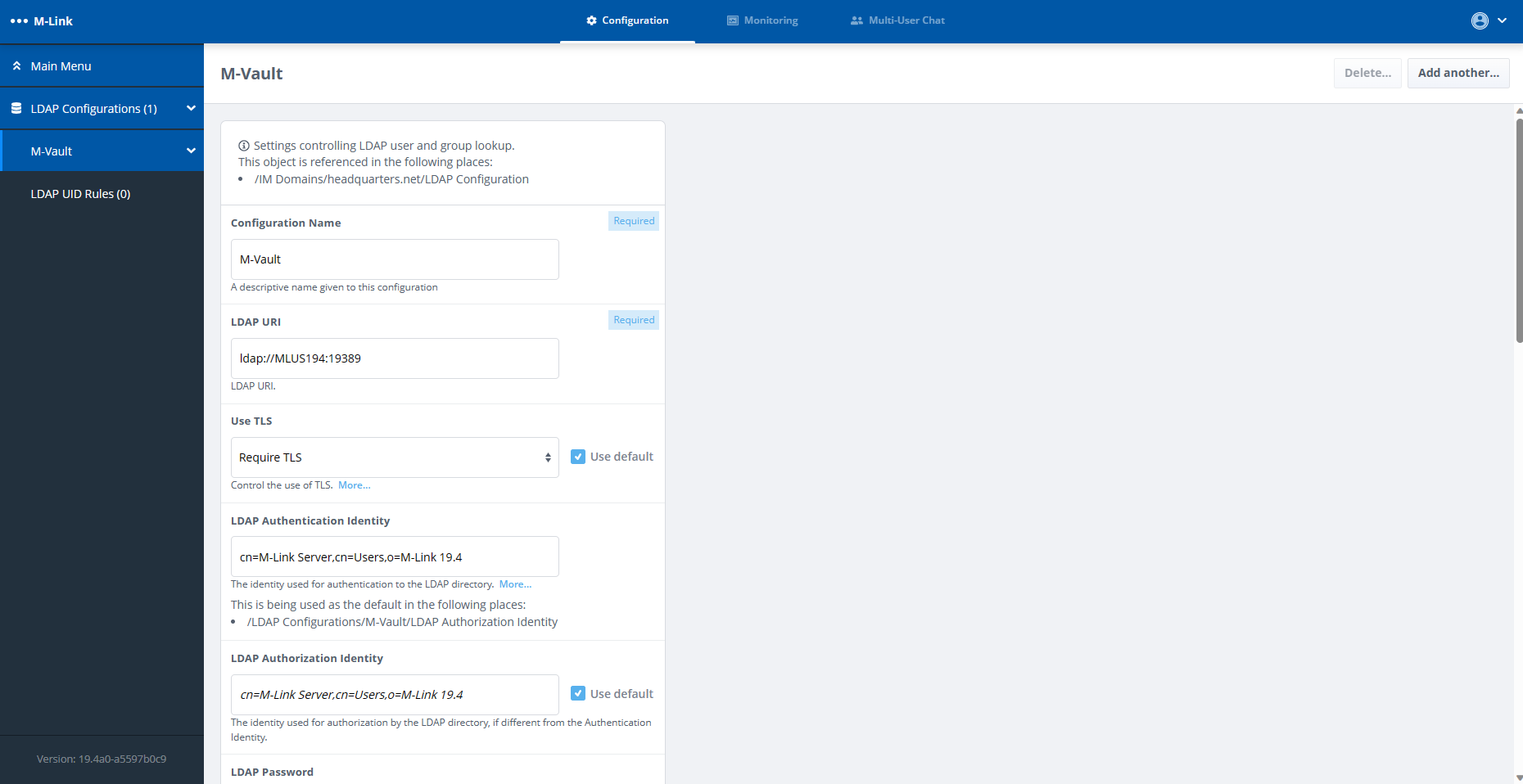
Network Control
When setting up a communications network security has to take priority, especially if that network is going to be used in a high security, or volatile environment. We design our Cross Domain Guards with this high security focus in mind, giving you a deep level of control over what comes in to and goes out of your network.
High Availability
Our Cross Domain Guards are made to be flexible in their deployment. So whether you need to deploy a single instance, or multiple guards in a ‘high availability’ setup, the deployment process is designed to fit into your existing network as seamless as possible.
Read the latest Whitepapers

Ready to request an Evaluation?
We welcome evaluations of our products and will make support resources available to you for the duration of your evaluation.